Galbanum
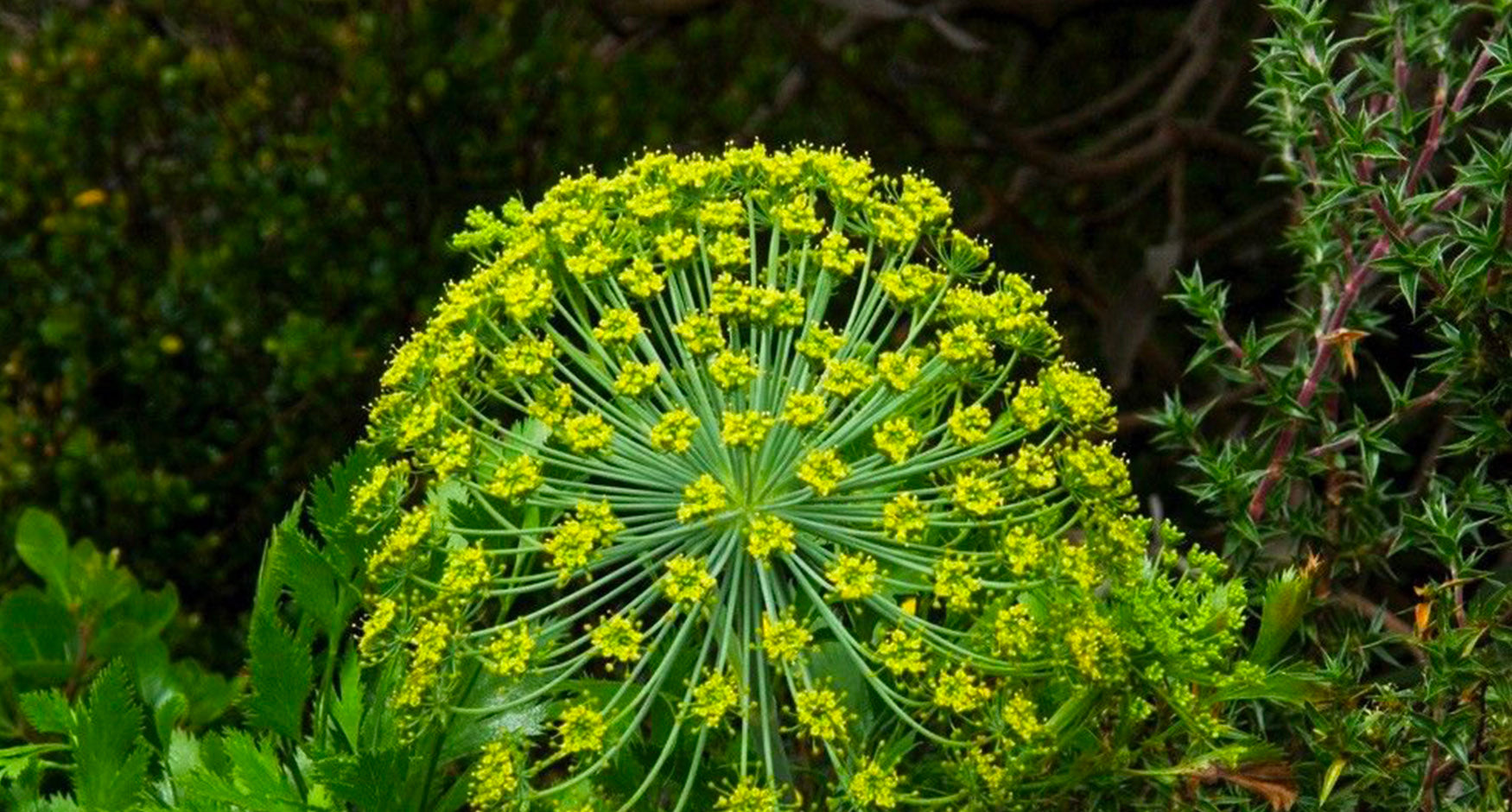

The plant :
Galbanum (Ferrula Gummosa) is a member of the Umbelliferae family. It is a perennial herb reaching one meter in height and diameter. Originally Elburz mountains in Northern Iran, galbanum thrives in a desertic and mountainous environment. Hermaphroditic plant, its flowering period extends from July to September when one sees appear flowers in yellow parasols with a not very pleasant smell.
In History :
Galbanum has many medicinal properties (expectorant, stimulant, agglunative, etc.) that men have learnt to use from very early on. Galbanum was found in many ointments formulae from ancient Egypt. In Europe, during the Middle Age and Modern Times, galbanum was involved in many recipes for medicines.
Some examples :
Making of Archigenes
Castoreum, long black pepper, siorax, spica nard, costus, galbanum & opium.
Saffron. Skimmed honey cooked in a soft electuary consistency.
Make it an opiate
It is suitable for slaughtering and appeasing the hysterical vapors; it is used to calm the cough to stop the spitting of blood, the courts of belly, to resist corruption, to excite sleep.
The dose is from half-scrupulum until a dragme.
Universal pharmacopeia (1684)
Emulsion of Galbanum
Ingredients: Galbanum, dry sprayed, 32 grams. Water, 1 liter.
Preparation: Divide the galbanum with a little water by trituration; add the water little by little; decant; repeat the trituration as many times as necessary, so that the emulsion is homogeneous.
Dosage: 2 to 3 cups a day.
Cared for : Stridulous angina; Wet asthma; Chronic bronchitis ; Bronchorrhea Chlorosis; Flatulent colic; Constipation; Whooping cough; Chronic cystitis; Dysmenorrhea; Hypochondria; Hysteria; Spasm; Spasmodic cough.
Treatise of the properties of the most effective medical plants for the maintenance and restoration of health (1886)
In perfumery :
Galbanum is harvested through incision of the root from which a milky, highly odorous liquid is extracted, either by distillation to obtain an essential oil or by solvent extraction to obtain a dark resinoid with a green, earthy and woody smell.
In perfumery, galbanum can recreate floral notes but its main use is to give a green note to the perfume. The perfumer must however use it with great caution as it can quickly stifle the other notes.
The many olfactory facets of Galbanum (green, woody, balsamic, animal, herbaceous, woody) allow the perfumer to use it in different ways: playing on the green side of the note, galbanum brings freshness and dynamism to a perfume by playing on the earthy side and bringing an intense woody note.






Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.